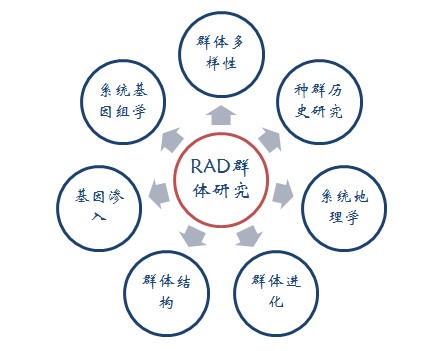
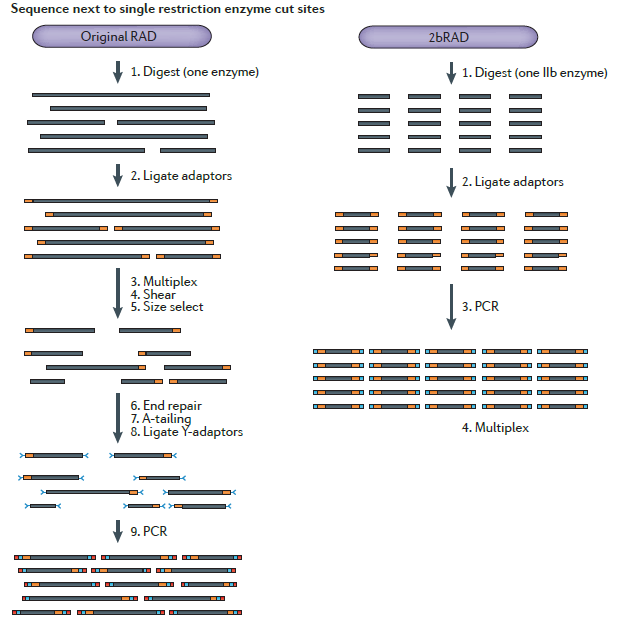
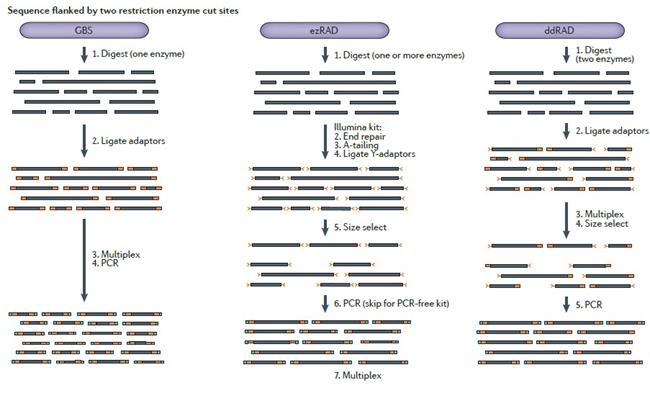
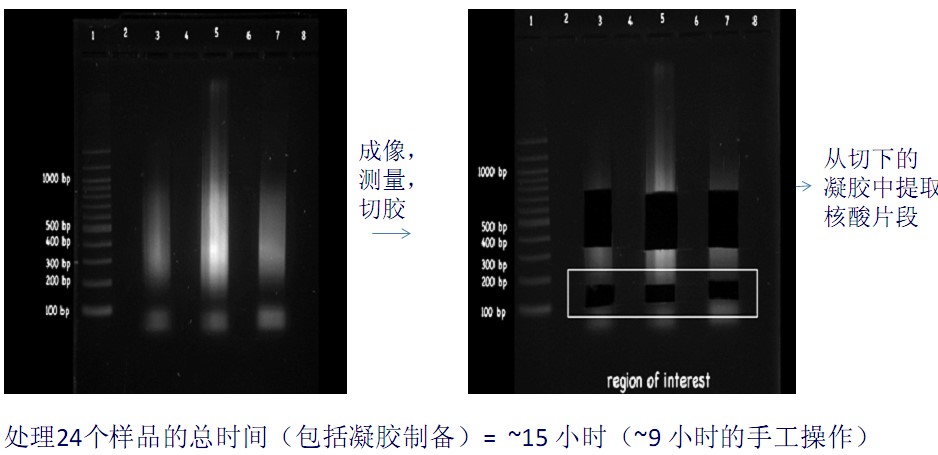
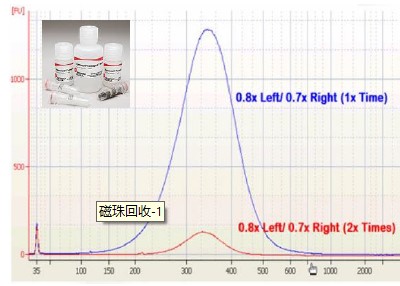
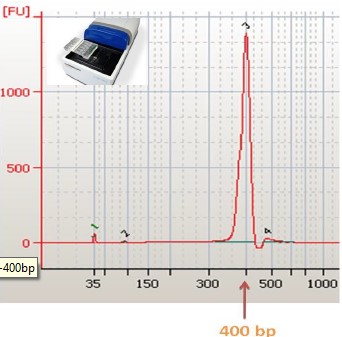
Application of Sage Science Nucleic Acid Fragment Recovery System in RADseq
We are a specialized manufacturers of Animal Extract from China; We support Animal Organ Extract, Animal Protein Powder, Velvet Antler Extract, Deer Whip Extract, Marine Fish Collagen and so on. With advanced R & D and manufacturing in Animal Extract. With high-quality products of Animal Extract Raw Material, we can be a trust suppliers / factory. As a wholesale of Animal Extract, we have the perfect after-sales service and technical support. Look forward to your cooperation! Velvet Antler Extract,Animal Organ Extract,Deer Whip Extract,Marine Fish Collagen,Animal Protein Powder Xi'an Quanao Biotech Co., Ltd. , https://www.quanaobio.com