Experts teach you about balanced fertilization - wheat
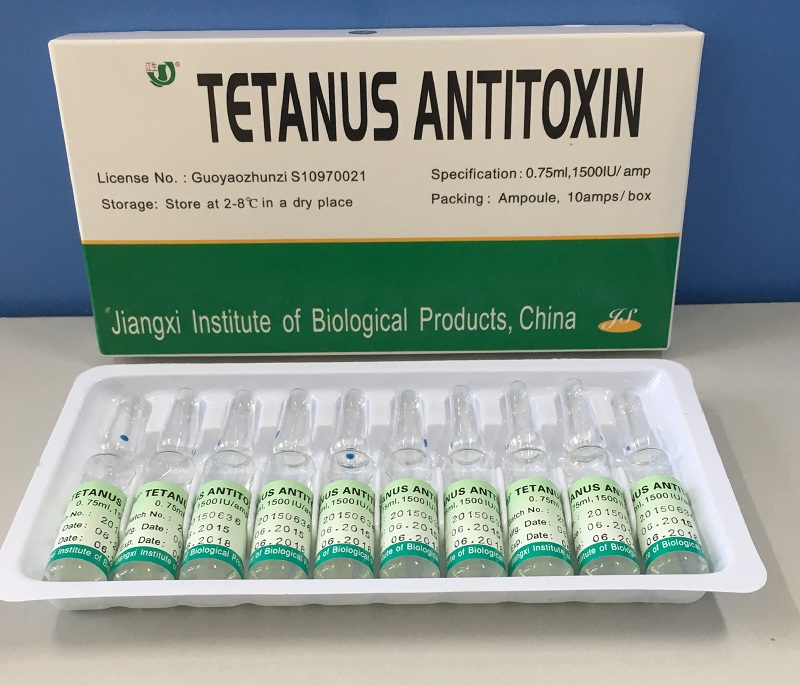
The main ingredient of Tetanus Antitoxin is that horse tetanus immunboglobulin following pepsin digestion. It's used for the prophylaxsis and therapy of tetanus.
The ATS Injection (equine origin) is efficient and affordable for patients, which maket share covers over 70% of China, and it's expored to over 20 countries, especially to Afica, southeast Asia, South Asia. We offer an array of Tetanus Antitoxin Injection in different strength, there are 1500IU, 3000IU, 5000IU, 10000IU.
Antitoxin Formulations For Human Antitoxin Formulations For Human,Tetanus Antitoxin,Tetanus Antitoxin Formulations,Antitoxin Formulations Essential Drug Jiangxi Institute of Biological Products Inc. , https://www.jxinstitute.com
According to the fertility law and nutritional characteristics of wheat, base fertilizer should be re-used and topdressing should be applied early. The amount of basal fertilizer should generally account for 60-80% of the total amount of fertilizer and topdressing for 40-20%. Basal fertilizer should be dominated by farmyard fertilizers, combined with chemical fertilizers.
The amount of nutrients absorbed by wheat during different growth periods is different. Generally, the amount of nutrients absorbed by seedlings is relatively small. After absorption, the absorption gradually increases, and the maximum absorption occurs from jointing to flowering, and the speed is fastest. Potassium absorbs its maximum value before the flowering.
First, the fertilization of wheat is carried out in a coarse and fine combination with the combination of nitrogen and phosphorus. The method of using crude fertilizer, nitrogen fertilizer, and phosphate fertilizer “three fertilizers to sit on the bottom†is a significant measure to increase production, and it is also an effective means to cultivate strong seedlings before winter. The application of organic fertilizers can cultivate fertility and improve soil structure. It is one of the fundamental ways to build stable and high-yield farmland. Therefore, in line with the principle of "coarse fat, supplemented by chemical fertilizers", various sources can be used to broaden the sources of fertilizer and provide enough base fertilizer for wheat fields. The wheat fields that are normally replanted with chemical fertilizers (especially ammonium monohydrogen phosphate) tend to grow faster, grow stronger, and have fewer dead seeds in winter, have higher percentage of spikes, and have a significant increase in yield. Moreover, the method is simple and can make up for the disadvantages of high volatility of ammonium bicarbonate, easy dissipation of fertilizer effect and inconvenience of top dressing. Generally, the clay soil with strong fertility retention ability can be applied to the bottom of more than half of the total amount of nitrogen fertilizer in the whole growth period; the sandy soil with poor fertilizer retention capacity is appropriately less, accounting for about 40% of the total amount of nitrogen fertilizer in the whole period. The bottom is appropriate. The application of phosphate fertilizers is a new increase in wheat production measures, especially in poor phosphorus soils, breakthroughs in the use of phosphate fertilizers, and the combination of nitrogen and phosphorus to increase production. According to a large number of experiments, the wheat fields with a yield of more than 500 kilograms per mu require more than 5000 kg of high-quality soil-fertilizer, 50 kg of standard nitrogen and phosphate fertilizer, and about 10 kg of potassium sulfate.
Second, return green fertilizer to be applied by seedlings. For weaker 2-3m seedlings or weak fertility in the pre-winter period and early decomposing and defertilizing of the wheat seedlings, early application and heavy application of green manure should be applied, and when the surface begins to defrost, it can be grabbed and applied (top fertilizer). Generally about 20 kg of ammonium bicarbonate can be traced per acre, and phosphorus-deficient wheat should be mixed with about 15 kg of superphosphate per acre. The best conditions for the application of diammonium phosphate 10-15 kg per mu. Returning green manure plays an important role in promoting the transformation of wheat seedlings from weak to strong and increasing the number of mu ears. However, for the seedlings with a higher number of seedlings, or wheat fields that are prosperous and not de-fertilized, green manure is not applied. Should be postponed until the time when he got up, to control the invalid childbirth, to improve the rate of tiller to ear, increase the number of acres of purpose.
Third, the rational use of fertilizer. The mid-term is the period when winter wheat needs the most water and fertilizer. The demand for water accounts for about 35% of the total amount, and the required fertilizer accounts for about 50% of the total amount. Especially in the jointing and booting stages, it is very sensitive to water reactions. Per acre chase standard nitrogen fertilizer (ammonium sulfate) about 15 kg.
Fourth, outside the top dressing. Phosphorus sprayed from the root has obvious effect of increasing production. After the flowering, the secondary phosphorus fertilizer is sprayed. The grain weight can increase by 2-3 grams, and the yield increases by 10%.