Post-disaster vegetable field management measures
Lithium Hydroxide CAS No.1310-65-2 Lithium Hydroxide Basic Information
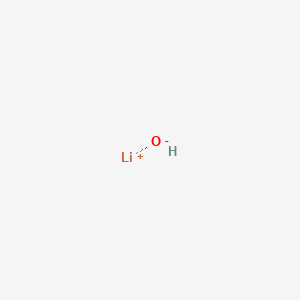
Lithium Hydroxide Structure
Stability: Stable. Incompatible with moisture. strong acids, carbon dioxide.
Uses of Lithium Hydroxide Lithium Hydroxide,Lithium Hydroxide Monohydrate,Lithium Hydroxide Formula,Lithium Hydroxide Uses,Lithium Hydroxide Price Shandong YingLang Chemical Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com
CAS: 1310-65-2
MF: LiOH
MW: 23.95
EINECS: 215-183-4
Mol File: 1310-65-2.mol
Melting point 462 °C
Boiling point 925°C
density 1.43
storage temp. Store at R.T.
solubility water: soluble71g/L at 20°C
form Solid
Specific Gravity 2.54
color White to light yellow
Used in the production of lithium salts and lithium-based greases, electrolytes for alkaline batteries, lithium bromide refrigerator absorption fluids, etc.
